Affiliate Marketing Cashback Model: How Platforms Earn and Users Save
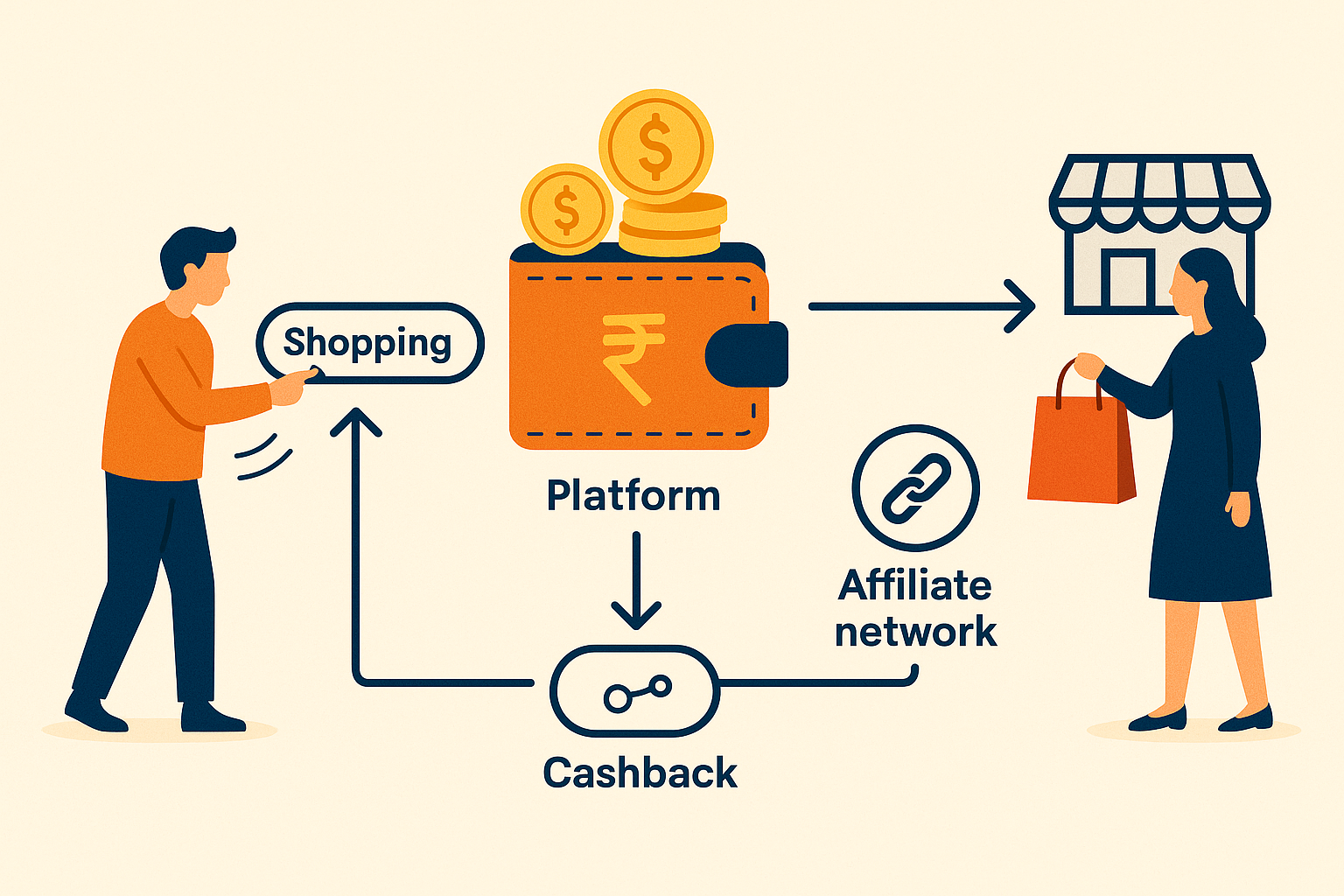
In Affiliate Marketing, Cashback platforms route tracked shopping journeys, collect commissions from affiliate networks or merchants, and share a defined portion with users. Retailers gain incremental orders and the platform earns from the retained margin.
For policy and disclosure basics, see the FTC Endorsement Guides. For tracking foundations such as app and web deep links, review Apple Universal Links and Android App Links.
Money flow 101
User click → Affiliate network → Retailer │ │ └── cashback credit ◄── Platform wallet (after validation)
A unique click identifier travels from the platform to the merchant through the network. After the order is validated and the return window passes, a confirmed commission triggers a wallet credit for the user based on the programme rules.
Revenue split and maths
Example on a $100 basket with an 8 percent commission. Exact percentages vary by category and partner agreements.
| Slice | Amount | % of commission |
|---|---|---|
| User cashback | $4.00 | 50% |
| Platform margin | $2.00 | 25% |
| Overheads and tax | $2.00 | 25% |
Some programmes show a provisional wallet credit while an order is pending. Final approval depends on merchant confirmation windows and fraud checks.
Why users save
- Net price drop without codes; cashback can apply on already discounted items.
- Stackable rewards with eligible card offers or brand loyalty points where terms allow.
- Referral bonuses that add incremental wallet earnings when friends shop.
How platforms earn more
- Tiered commission rates by hitting volume slabs with networks or direct programmes.
- Sponsored placements such as homepage tiles or email features on a fixed fee.
- Gift card spread when buying discounted vouchers and selling at face value.
- VIP plans that include faster withdrawals or enhanced rates for a subscription fee.
Tech stack quick view
- Core app on a mainstream web framework and relational database for offers, clicks, and wallets.
- Postback service to ingest merchant or network confirmations with idempotency and retries.
- Cache for fast click ID lookups during attribution.
- Feed sync jobs to refresh offers, coupons, and store terms on a schedule.
For server to server security patterns, HMAC is a common choice. See RFC 2104.
Risks and fixes
Tracking gaps
Prefer server to server confirmations. Add browser fallbacks and extension reminders where allowed.
Cash flow strain
Set clear lock periods and keep a reserve aligned to expected approvals. Offer vouchers or gift cards as an alternative withdrawal method if it suits the audience.
Abuse and self referrals
Use velocity rules, basic device signals, and referral-IP checks. Follow privacy guidance and avoid storing sensitive data unnecessarily.
Where the model heads next
- Card linked offers that credit based on eligible payment events rather than clicks.
- Real time partner APIs for faster confirmation instead of delayed batch files.
- Smarter wallets that suggest legitimate stacking options based on terms.
Conclusion
The cashback model converts a share of affiliate commission into shopper value. Retailers see incremental demand, users save, and platforms retain a margin when tracking, approval rules, and disclosures are clear.
Summary
- Map the end to end flow from click to confirmed payout and publish timelines.
- Define a transparent revenue split and surface it in user terms.
- Harden tracking with server to server postbacks and idempotency.
- Control risk with basic velocity checks and clear referral rules.
For implementation guidance or migration planning, contact Cusenware.
